The real estate is one of the industries inseparable from geodesy. This time in the series Geodata in business we decided to describe possible ways of applying modern geoinformatics solutions in sake of this particular industry. What data can be used in order to gain the most?
Spatial information could be presented in many ways. One of them is aerial imagery and airborne laser scanning data. They are the foundation for any further processed geospatial products, such as orthophotomaps, digital terrain models and digital surface models. Each way of data presentation and analysis is associated with different opportunities and potential benefits. What could be achieved and what data is worth using for ones operating within the real estate industry?
GEODATA IN REAL ESTATE
- Orthophotomap
It is a raster image of the terrain, resulting from the processing of aerial imagery or satellite imagery to the form of an image in orthogonal projection, so identical with a perspective of a traditional map. Commercially available aerial cameras enable for the acquisition of the imagery characterised by the ground sampling distance of a few centimetres. The equipment so far associated only with secret military missions or spy movies now is commonly used by geoinformation companies in order to meet the needs of various industries.
Properly interpreted data contained in the orthophotomap could provide detailed information on the current state of the immediate surroundings around the planned construction site. Especially, if the analysis is based on the most recent data, there is no longer the necessity of performing a field inspection. Moreover, the applied technology allows for applying different layers to the orthophotomap containing various information, e.g. data from the land and building register, which could be used for verifying the legal status of a given plot.
- Point clouds
Point clouds are acquired as the result of executing the airborne laser scanning missions. Each of the millions of registered points contains information about its exact spatial location. This is the type of data that lay the foundations for the preparation of three-dimensional object models, digital surface models and digital terrain models.

Due to that form of data presentation, investors can obtain precise information about the area chosen for the construction site. Such knowledge could be invaluable on the planning stage. One of many purposes of using a point clouds is calculating the number of trees in a designated area, as well as assessing their height, species affiliation and many other attributes. This allows for easily calculating the cost of felling and obtaining the necessary permits.
- Digital Surface Models
The digital surface model is a point reflection of the area’s surface, which also contains the information about all the elements located above the ground. Such models guarantee greater cost control as early as at the investment planning stage. Due to the opportunities resulting from precise measurement of the elements mapped on the digital surface model, analysing the investments fitting into the boundaries of the selected plot along with calculating the cubic capacity of the land for ground levelling becomes feasible.
- 3D mesh
Realistic three-dimensional mesh models in real colours could be used for the sake of analysis and acquisition of accurate data regarding the surroundings around the planned investment. However, the true potential of this data presentation form is demonstrated by using models for marketing purposes. Such presentation will help the individual client to imagine his presence in the place of the planned investment in a new, friendly location. Undoubtedly it will make a positive impact on generating interest and sales.
- Solar maps and noise maps
The process of collecting geodata for selected areas results in producing tens of terabytes. Such a vast amount of information allows qualified employees to develop analyses containing extra information about the surveyed area. Slightly less popular, but extremely useful for the real estate industry, may be the map of solar potential (we have written about suitability of geodata in photovoltaics HERE) and noise maps. Those types of geospatial products significantly increase the efficiency of the investment planning phase and allow for choosing the optimal location for the one’s needs. The noise level or solar potential can be of great importance to the end user of the building.
GEODATA AS A SUPPORT OF DUE DILIGENCE
The term due diligence is defined as the examination or audit of a potential investment. It aims at confirming all the facts regarding a sale in order to protect the interests of individuals or entities trying to close a deal. [1] The scope of the analysis may vary depending on a potential investor's approach to investment risk, as well as on their knowledge and experience. This verification is a valuable tool for supporting investment decisions. [2]
In relation to the real estate market, the aforementioned analysis assumes verification whether the content of the entries in the land and mortgage register is consistent with the actual state of affairs. Also a subject of the verification is the connection to the public road and communication network, development possibilities, information on environmental and landscape protection regulations and conservation and archaeological protection for the area prepared for the planned investment. The scope of due diligence is complemented by the analysis of documents provided by the seller, including contracts for the supply of utilities and services provided to the property.
Therefore, the analysis of the land for the investment is carried out within the following areas:
- legal status of the property,
- possible conservation protection,
- the planning situation,
- supply of utilities (water, sewage, gas, electricity),
- communication accessibility.
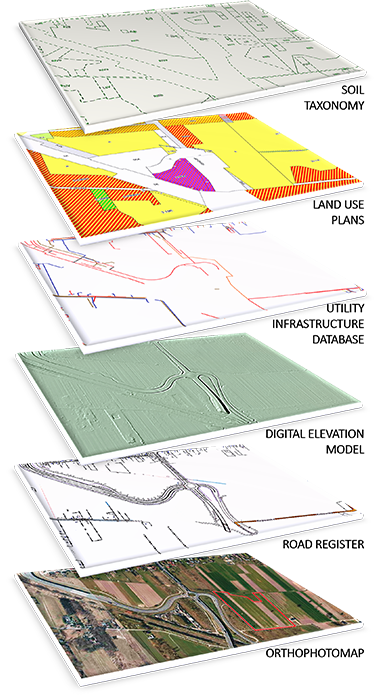
Although all information is unavailable in the form of geodata, more than half of the abovementioned areas could be prepared with the help of up-to-date and detailed spatial information. This makes them a useful tool during the process of due diligence analysis of the property. Aerial imagery is both a huge source of information about the location, as well as a foundation for additional spatial data, i.e. the distribution of water supply, sewage and energy networks or classification of communication routes. Such combination makes it feasible to measure the elements mapped in the pictures together with their relation to the aforementioned networks. Planning new locations for investments may be simpler than ever.
Contact us to select the required geodata in order to increase the efficiency of remote work and analysis of the planned investment’s location. The appropriate selection will allow for quick and seamless implementation of new solutions into everyday work.
- Karolina Wróbel
Business development specialist
karolina.wrobel@opegieka.pl
Notes:
[1] Brzozowska K. (2012), Due diligence jako źródło informacji w procesie podejmowania decyzji inwestycyjnych, Zeszyty Naukowe SGGW – Ekonomia i Organizacja Gospodarki Żywnościowej, nr 91, s. 17-26.
[2] Piątek E., Dziedzic-Jagocka I. (2015), Due diligence – źródła danych do analizy, Zeszyty Naukowe Uniwersytetu Szczecińskiego nr 855, „Finanse, Rynki Finansowe, Ubezpieczenia” nr 74, t. 1, Wydawnictwo Naukowe Uniwersytetu Szczecińskiego, Szczecin, s 653-660.


 European Union
European Union
